AI Agent와 MCP: LLM이 도구를 사용하는 방법
AI Agent란
AI Agent는 단순히 질문에 답하는 챗봇을 넘어서, 스스로 계획을 세우고 도구를 사용해 목표를 달성하는 시스템입니다. 텍스트 생성만 하는 LLM과 달리, Agent는 파일을 읽고, API를 호출하고, 코드를 실행할 수 있습니다. Claude Code나 Cursor 같은 AI 코딩 도구들이 바로 이런 Agent의 대표적인 예입니다.
Agent의 핵심 구성요소
1. 추론 엔진 (Reasoning Engine)
LLM이 핵심 두뇌 역할을 합니다. 사용자 요청을 분석하고, 어떤 도구를 어떤 순서로 사용할지 결정합니다. 이 과정에서 Chain of Thought(CoT) 추론을 활용해 복잡한 문제를 단계별로 분해합니다.
2. 메모리 (Memory)
Agent는 두 종류의 메모리를 활용합니다.
| 종류 | 설명 | 구현 방식 |
|---|---|---|
| Working Memory | 현재 대화의 컨텍스트 | LLM의 context window |
| Persistent Memory | 장기 기억 | Vector DB (Pinecone, Weaviate, Chroma) |
Vector DB는 텍스트를 임베딩 벡터로 변환해 저장합니다. 쿼리가 들어오면 코사인 유사도로 관련 문서를 검색해 LLM에 전달합니다.
# 임베딩 생성 및 저장 예시
embedding = openai.embeddings.create(
model="text-embedding-3-small",
input="사용자가 React를 선호한다고 했음"
)
vector_db.upsert(id="user_pref_1", values=embedding.data[0].embedding)
3. 도구 (Tools)
Agent가 외부 세계와 상호작용하는 인터페이스입니다. OpenAI의 Function Calling, Anthropic의 Tool Use가 대표적입니다.
// Anthropic Tool Use 스키마 예시
const tools = [
{
name: "execute_sql",
description: "PostgreSQL 데이터베이스에서 SQL 쿼리를 실행합니다",
input_schema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
query: {
type: "string",
description: "실행할 SQL 쿼리. SELECT만 허용됩니다."
},
database: {
type: "string",
enum: ["production", "staging"],
description: "대상 데이터베이스"
}
},
required: ["query", "database"]
}
}
]
4. ReAct 패턴
Agent는 Thought → Action → Observation 루프를 반복합니다. 2022년 Yao et al.의 논문에서 제안되어 ICLR 2023에서 발표된 ReAct(Reasoning + Acting) 패턴이 표준으로 자리잡았습니다.
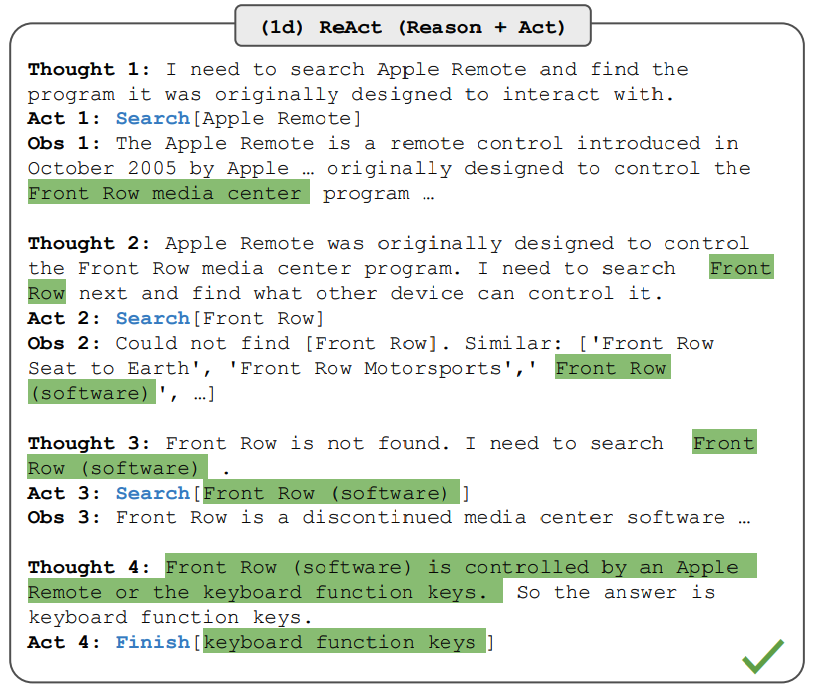
[Loop Start]
Thought: 사용자가 최근 주문 내역을 요청했다.
orders 테이블에서 user_id로 조회해야 한다.
Action: execute_sql
Action Input: {
"query": "SELECT * FROM orders WHERE user_id = 123 ORDER BY created_at DESC LIMIT 5",
"database": "production"
}
Observation: [
{"order_id": 456, "product": "MacBook Pro", "amount": 2500000, "created_at": "2025-03-28"},
{"order_id": 455, "product": "AirPods", "amount": 250000, "created_at": "2025-03-15"}
]
Thought: 2건의 주문 내역을 받았다. 사용자에게 요약해서 전달하자.
Final Answer: 최근 주문 내역입니다:
1. MacBook Pro (250만원) - 3월 28일
2. AirPods (25만원) - 3월 15일
[Loop End]
루프 종료 조건은 보통 다음 중 하나입니다:
- LLM이
Final Answer를 반환 - 최대 반복 횟수(예: 10회) 도달
- 타임아웃
MCP (Model Context Protocol)
왜 필요한가
AI 모델은 기본적으로 외부 데이터에 접근할 수 없습니다. 각 AI 앱마다, 각 데이터 소스마다 별도의 통합 코드를 작성해야 합니다. N개의 AI 앱 × M개의 데이터 소스 = N×M개의 통합이 필요한 셈입니다.
MCP는 이 문제를 해결합니다. 한 번 구현한 MCP 서버는 모든 MCP 호환 클라이언트(Claude Desktop, Cursor, Windsurf 등)에서 재사용할 수 있습니다. IDE가 Language Server Protocol(LSP)로 다양한 언어를 지원하듯, AI 앱은 MCP로 다양한 도구를 지원합니다.
프로토콜 아키텍처
MCP는 Host-Client-Server 3계층 구조입니다.
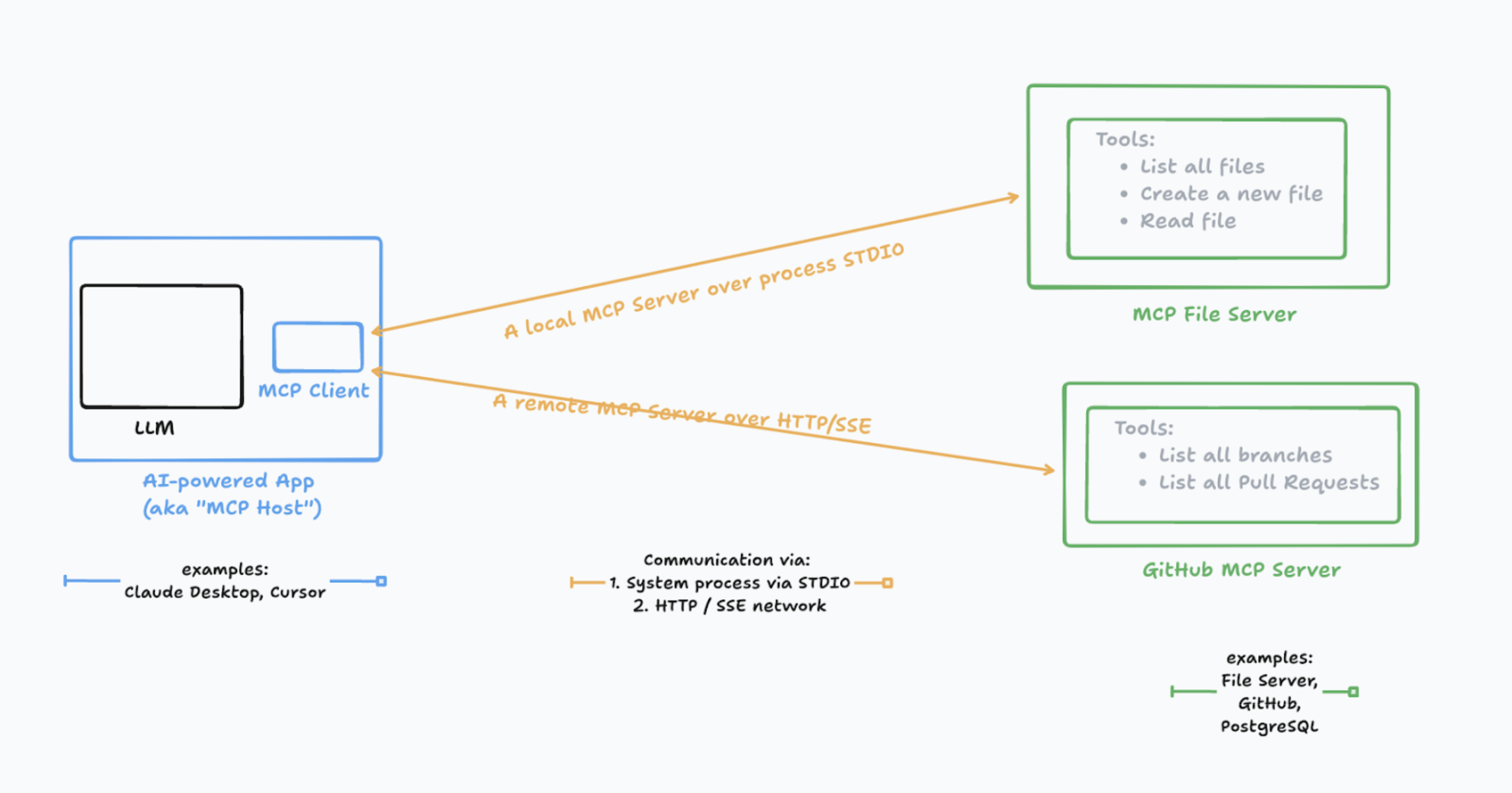
| 구성요소 | 역할 | 예시 |
|---|---|---|
| Host | AI 애플리케이션, 여러 Client를 관리 | Claude Desktop, Cursor |
| Client | Server와 1:1 연결 유지, 메시지 라우팅 | Host 내부 컴포넌트 |
| Server | 특정 기능(도구, 리소스) 제공 | filesystem-server, github-server |
하나의 Host가 여러 Client를 가질 수 있고, 각 Client는 하나의 Server와 연결됩니다.
Transport Layer
MCP는 두 가지 전송 방식을 지원합니다.
1. stdio (Standard I/O)
로컬에서 서버를 자식 프로세스로 실행합니다. stdin/stdout으로 통신합니다.
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["./mcp-server/index.js"],
"env": { "HOME": "/Users/dev" }
}
}
}
2. HTTP + Server-Sent Events (SSE)
원격 서버와 통신할 때 사용합니다. 클라이언트→서버는 HTTP POST, 서버→클라이언트는 SSE로 스트리밍합니다.
Client Server
│ │
│──── POST /message ───────────>│ (요청)
│ │
│<─── SSE event: result ────────│ (응답 스트리밍)
│<─── SSE event: progress ──────│
│<─── SSE event: done ──────────│
JSON-RPC 2.0 메시지 포맷
MCP의 모든 통신은 JSON-RPC 2.0 기반입니다.
요청 (Request)
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "read_file",
"arguments": {
"path": "/etc/hosts"
}
}
}
응답 (Response)
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "127.0.0.1 localhost\n..."
}
]
}
}
에러 응답
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"error": {
"code": -32602,
"message": "Invalid path: access denied"
}
}
초기화 핸드셰이크
클라이언트와 서버가 연결되면 capability negotiation이 이루어집니다.
Client Server
│ │
│── initialize ────────────────>│
│ { │
│ "protocolVersion": "2024-11-05",
│ "capabilities": { │
│ "sampling": {} │ (클라이언트가 지원하는 기능)
│ }, │
│ "clientInfo": { │
│ "name": "claude-desktop",
│ "version": "1.0.0" │
│ } │
│ } │
│ │
│<─────────────── result ───────│
│ { │
│ "protocolVersion": "2024-11-05",
│ "capabilities": { │
│ "tools": {}, │ (서버가 지원하는 기능)
│ "resources": {} │
│ }, │
│ "serverInfo": { │
│ "name": "filesystem", │
│ "version": "1.0.0" │
│ } │
│ } │
│ │
│── initialized ───────────────>│ (핸드셰이크 완료 알림)
Server Capabilities
서버가 제공할 수 있는 기능들입니다.
| Capability | 설명 |
|---|---|
tools |
실행 가능한 함수 (파일 생성, API 호출 등) |
resources |
읽기 전용 데이터 (파일 내용, DB 레코드 등) |
prompts |
미리 정의된 프롬프트 템플릿 |
logging |
서버 로그를 클라이언트에 전송 |
tools/list 응답 예시
{
"tools": [
{
"name": "create_file",
"description": "새 파일을 생성합니다",
"inputSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"path": { "type": "string" },
"content": { "type": "string" }
},
"required": ["path", "content"]
}
}
]
}
Client Capabilities
클라이언트가 서버에게 제공하는 기능입니다.
| Capability | 설명 |
|---|---|
sampling |
서버가 LLM 호출을 요청할 수 있음 |
roots |
서버가 접근 가능한 파일시스템 경로 |
sampling은 서버가 클라이언트의 LLM을 호출해 텍스트를 생성하도록 요청하는 기능입니다. Agentic한 동작을 가능하게 합니다.
MCP 서버 구현
TypeScript SDK
import { Server } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/index.js";
import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js";
import {
ListToolsRequestSchema,
CallToolRequestSchema,
ErrorCode,
McpError
} from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/types.js";
import * as fs from "fs/promises";
import * as path from "path";
const ALLOWED_DIR = "/Users/dev/workspace";
const server = new Server(
{ name: "secure-filesystem", version: "1.0.0" },
{ capabilities: { tools: {} } }
);
// 경로 검증 함수
function validatePath(filePath: string): string {
const resolved = path.resolve(filePath);
if (!resolved.startsWith(ALLOWED_DIR)) {
throw new McpError(
ErrorCode.InvalidParams,
`Access denied: ${filePath} is outside allowed directory`
);
}
return resolved;
}
// 도구 목록
server.setRequestHandler(ListToolsRequestSchema, async () => ({
tools: [
{
name: "read_file",
description: "파일 내용을 읽습니다. UTF-8 텍스트 파일만 지원합니다.",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
path: {
type: "string",
description: "읽을 파일의 절대 경로"
}
},
required: ["path"]
}
},
{
name: "write_file",
description: "파일에 내용을 씁니다. 기존 파일은 덮어씁니다.",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
path: { type: "string" },
content: { type: "string" }
},
required: ["path", "content"]
}
},
{
name: "list_directory",
description: "디렉토리 내용을 조회합니다.",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
path: { type: "string" }
},
required: ["path"]
}
}
]
}));
// 도구 실행
server.setRequestHandler(CallToolRequestSchema, async (request) => {
const { name, arguments: args } = request.params;
try {
switch (name) {
case "read_file": {
const filePath = validatePath(args.path as string);
const content = await fs.readFile(filePath, "utf-8");
return {
content: [{ type: "text", text: content }]
};
}
case "write_file": {
const filePath = validatePath(args.path as string);
await fs.writeFile(filePath, args.content as string, "utf-8");
return {
content: [{ type: "text", text: `Written: ${filePath}` }]
};
}
case "list_directory": {
const dirPath = validatePath(args.path as string);
const entries = await fs.readdir(dirPath, { withFileTypes: true });
const list = entries.map(e =>
`${e.isDirectory() ? "[DIR]" : "[FILE]"} ${e.name}`
).join("\n");
return {
content: [{ type: "text", text: list }]
};
}
default:
throw new McpError(ErrorCode.MethodNotFound, `Unknown tool: ${name}`);
}
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof McpError) throw error;
throw new McpError(
ErrorCode.InternalError,
error instanceof Error ? error.message : "Unknown error"
);
}
});
// 서버 시작
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await server.connect(transport);
console.error("MCP server started");
Python SDK
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
from mcp.types import Tool, TextContent
import os
ALLOWED_DIR = "/Users/dev/workspace"
app = Server("secure-filesystem")
def validate_path(file_path: str) -> str:
resolved = os.path.abspath(file_path)
if not resolved.startswith(ALLOWED_DIR):
raise ValueError(f"Access denied: {file_path}")
return resolved
@app.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> list[Tool]:
return [
Tool(
name="read_file",
description="파일 내용을 읽습니다",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"path": {"type": "string", "description": "파일 경로"}
},
"required": ["path"]
}
)
]
@app.call_tool()
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict) -> list[TextContent]:
if name == "read_file":
path = validate_path(arguments["path"])
with open(path, "r") as f:
content = f.read()
return [TextContent(type="text", text=content)]
raise ValueError(f"Unknown tool: {name}")
async def main():
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await app.run(read_stream, write_stream)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
asyncio.run(main())
보안 고려사항
1. Path Traversal 방지
// 취약한 코드
const content = await fs.readFile(userInput); // ../../../etc/passwd 가능
// 안전한 코드
const resolved = path.resolve(ALLOWED_DIR, userInput);
if (!resolved.startsWith(ALLOWED_DIR)) {
throw new Error("Access denied");
}
const content = await fs.readFile(resolved);
2. Prompt Injection 대응
악의적인 입력이 도구 실행을 유도할 수 있습니다. 서버는 입력을 신뢰하지 말고 검증해야 합니다.
// SQL Injection 방지
server.setRequestHandler(CallToolRequestSchema, async (request) => {
const { query } = request.params.arguments;
// SELECT만 허용
if (!query.trim().toUpperCase().startsWith("SELECT")) {
throw new McpError(ErrorCode.InvalidParams, "Only SELECT queries allowed");
}
// Prepared Statement 사용
// const result = await db.query(query); // 위험: SQL Injection 가능
const result = await db.query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = $1", [userId]); // 안전
});
3. 인증/인가
HTTP Transport 사용 시 OAuth 2.1 기반 인증을 구현할 수 있습니다.
// Authorization 헤더 검증
const authHeader = request.headers.get("Authorization");
if (!authHeader?.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
return new Response("Unauthorized", { status: 401 });
}
const token = authHeader.slice(7);
const payload = await verifyJWT(token);
if (!payload.scopes.includes("mcp:tools")) {
return new Response("Forbidden", { status: 403 });
}
주요 Agent 프레임워크
| 프레임워크 | 특징 | MCP 지원 |
|---|---|---|
| LangChain | LLM + 도구 체이닝, 가장 큰 생태계 | O (langchain-mcp-adapters) |
| LangGraph | 상태 머신 기반 복잡한 워크플로우 | O (공식 지원) |
| AutoGen | 멀티 Agent 협업 (Microsoft) | - (계획 중) |
| Semantic Kernel | .NET/Python 기반, 엔터프라이즈 | - (계획 중) |
| CrewAI | 역할 기반 멀티 Agent | - (미발표) |
마무리
AI Agent는 LLM에 실행 능력을 부여하는 기술입니다. ReAct 패턴으로 추론과 행동을 반복하며, 도구를 통해 외부 세계와 상호작용합니다.
MCP는 Agent와 도구 간의 표준 프로토콜입니다. JSON-RPC 2.0 기반의 명확한 스펙, Capability Negotiation, 다양한 Transport 지원으로 확장성을 갖췄습니다.
2024년 11월 Anthropic이 공개한 이후, OpenAI, Google, Microsoft가 모두 지원을 발표하면서 사실상 표준으로 자리잡고 있습니다.
